

Removal of the need for hydrogen storage systems as hydrogen is generated on demand by water c MIIT Key Laboratory of Critical Materials Technology for New Energy Conversion and Storage, State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, P.Reduction of environmental damage caused by fossil fuel combustion products.Small hydrogen productions for laboratories.are performed by the CASTEP module in the Materials Studio (version 8.0).
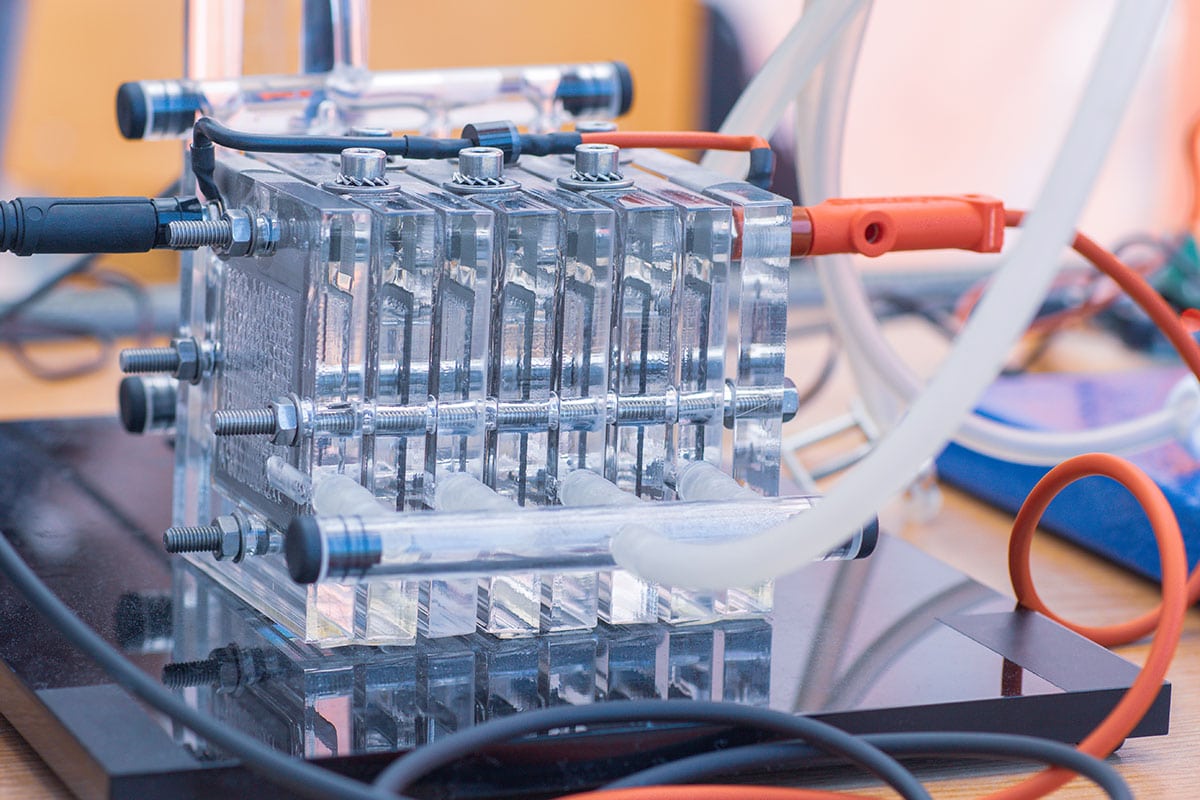
Supply of hydrogen to devices where there is not hydrogen distribution like remote areas or emergency zones Hydrogen, as a high-density green energy produced from water splitting with.Hydrogen generation as fuel for small devices that operate with fuel cells.Encouraging processes have been developed in the last decade for the photocatalytic production of H 2 O 2. The proposed innovation allows to overcome the critical issues connected with the storage of hydrogen on devices operating with fuel cells. The production of H 2 O 2 by photocatalysis is a sustainable process, since it uses water and oxygen as the source materials and solar light as the energy. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the process of producing such a composite material which requires low energy consumption and a high level of cleaning. Other process emissions occur from using carbon-based materials as reaction. Linyou Cao, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and senior author of a paper. Such a composite material generates hydrogen and heat in room temperature water and without the use of potentially toxic and/or hazardous chemical catalysts. carbon-free hydrogen produced with electrolysis and renewable electricity. (A Q&A with Cao on how this research differs from earlier studies of other catalysts for hydrogen production can be found on NC State’s research blog.) We found that the thickness of the thin film is very important, says Dr. Such a composite material is capable of generating hydrogen and heat in situ from safe and widely available sources, such as water. The invention comprises a graphene-based composite material, in which the graphene has the surface covered by a metal film.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
